The production of plastic bottles is a highly versatile process, offering a range of methods to suit diverse bottle shapes, sizes, materials, locations, and cost considerations. While each manufacturing technique has its unique nuances, the core principles remain similar: plastic pellets (also known as resin) are heated and then shaped into the desired bottle form using extrusion, injection, or blow molding processes. COMPAX specializes in various manufacturing methods, including Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM), Injection Blow Molding (IBM), Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM), Co-Extrusion (Co-Ex), and Injection Molding (IM). Let’s explore each of these processes in detail:
Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM) #
In the extrusion blow molding process, a continuous, hollow, round tube of plastic called a “parison” is formed. Here’s how it works:
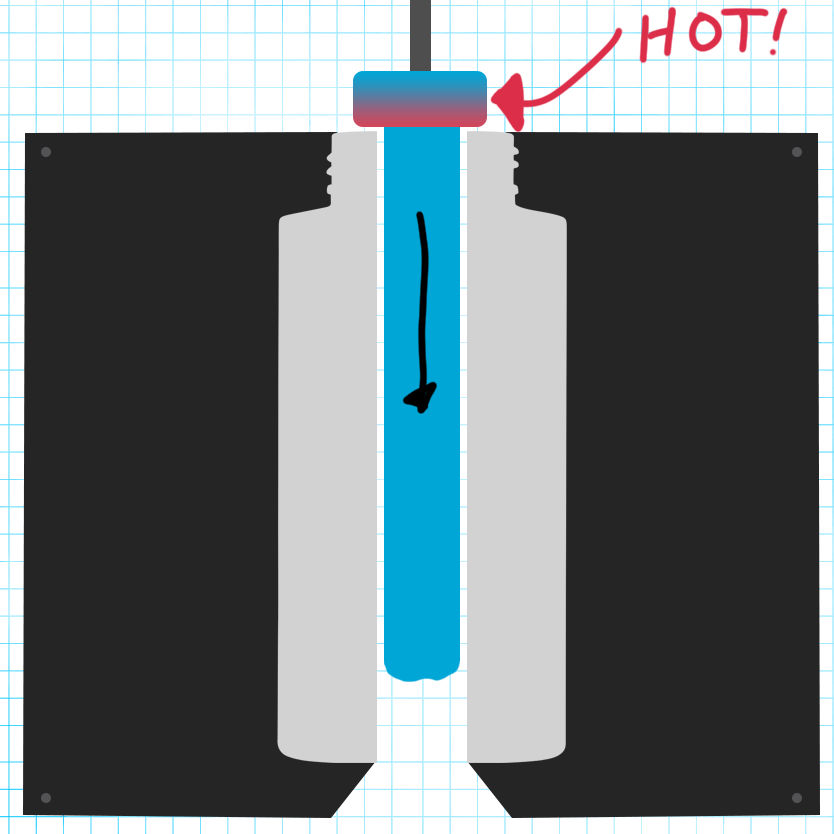 Parison Formation: Plastic pellets are melted, and the molten plastic is extruded to create the parison.
Parison Formation: Plastic pellets are melted, and the molten plastic is extruded to create the parison.
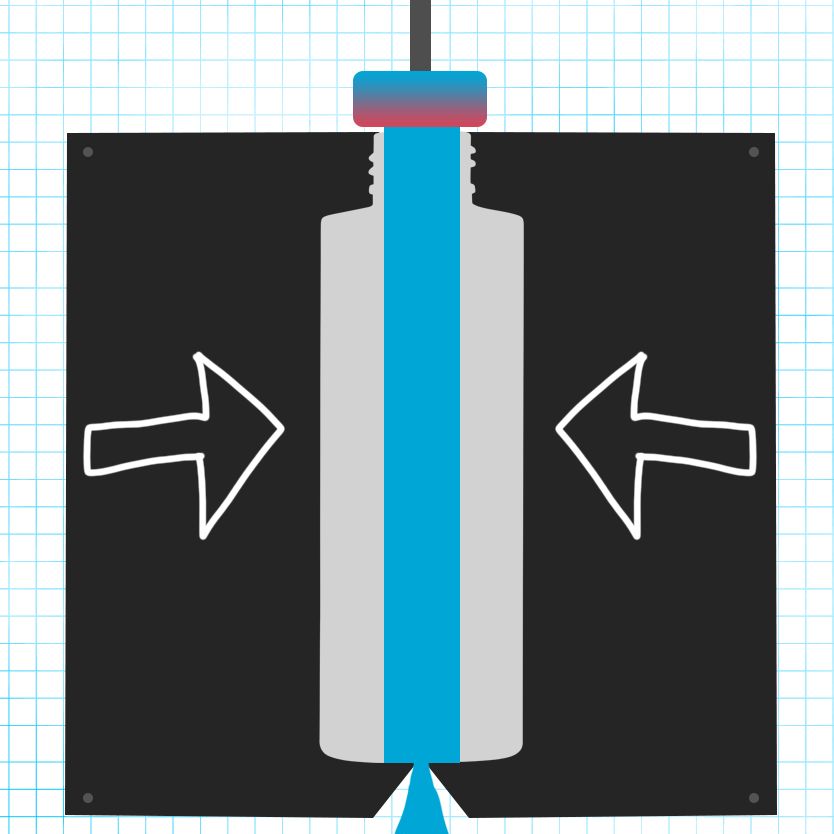 Mold Clamping: The two halves of the mold clamp together around the parison, pinching one end shut.
Mold Clamping: The two halves of the mold clamp together around the parison, pinching one end shut.
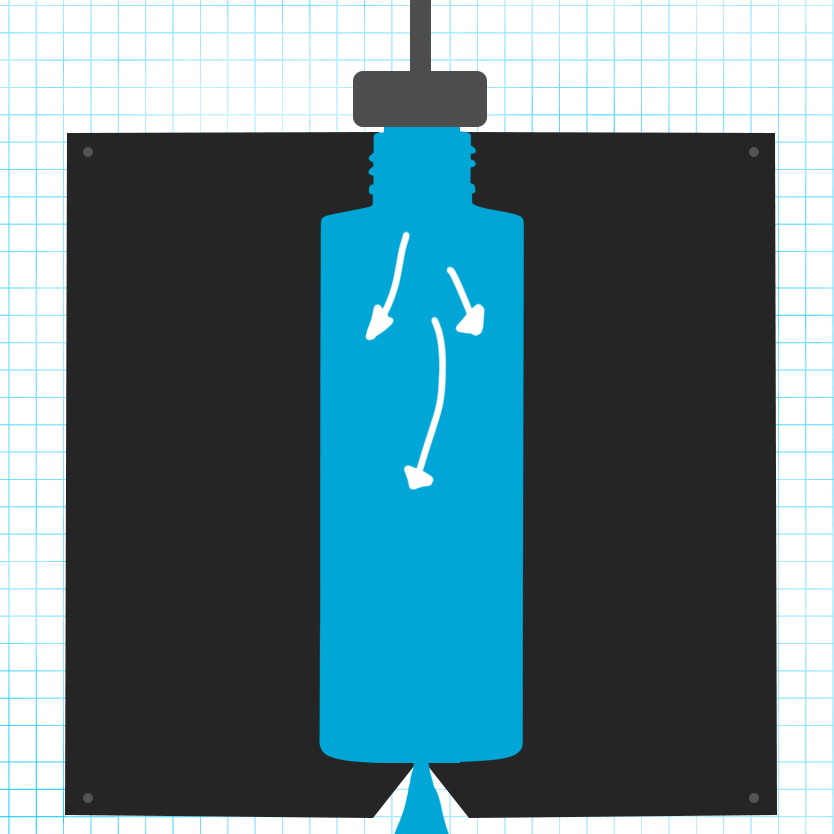 Air Injection: Air is blown into the open end of the parison, expanding it to conform to the mold cavities. This results in the desired bottle shape.
Air Injection: Air is blown into the open end of the parison, expanding it to conform to the mold cavities. This results in the desired bottle shape.
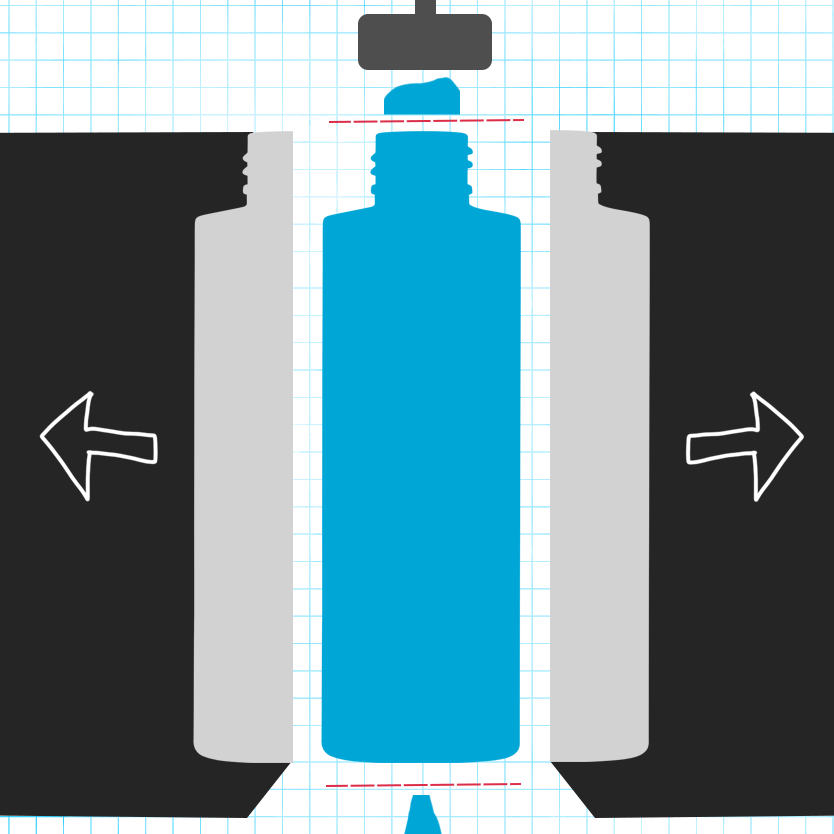 Cooling and Removal: Once the bottles are formed and sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the bottles are removed. Occasionally, excess plastic (known as “flash”) may be present around the edges of the bottle.
Cooling and Removal: Once the bottles are formed and sufficiently cooled, the mold opens, and the bottles are removed. Occasionally, excess plastic (known as “flash”) may be present around the edges of the bottle.
 Flash Handling: Flash is a normal part of the EBM process and occurs when the mold closes around the parison. It can be found around the bottle’s neck block (referred to as “moil”) or at the base of the bottle (“tail”). Moils and tails are often reprocessed during production, a practice known as using “regrind.”
Flash Handling: Flash is a normal part of the EBM process and occurs when the mold closes around the parison. It can be found around the bottle’s neck block (referred to as “moil”) or at the base of the bottle (“tail”). Moils and tails are often reprocessed during production, a practice known as using “regrind.”
Materials typically used for EBM bottles include PE, PP, and PET. EBM bottles may exhibit a seam along the bottom or sides due to the manufacturing process.
Injection Blow Molding (IBM) #
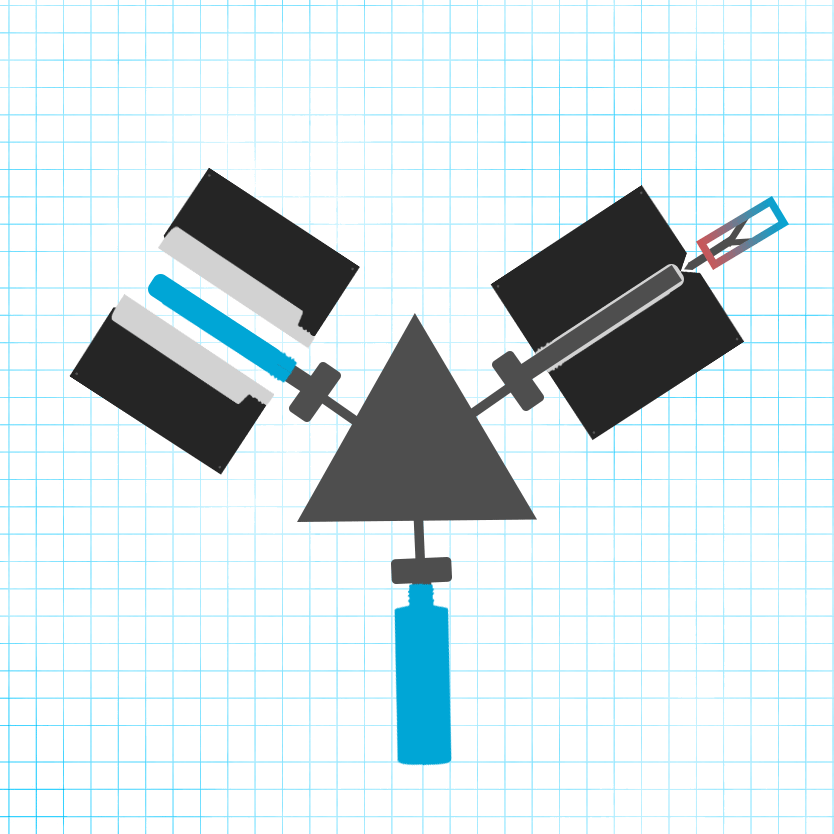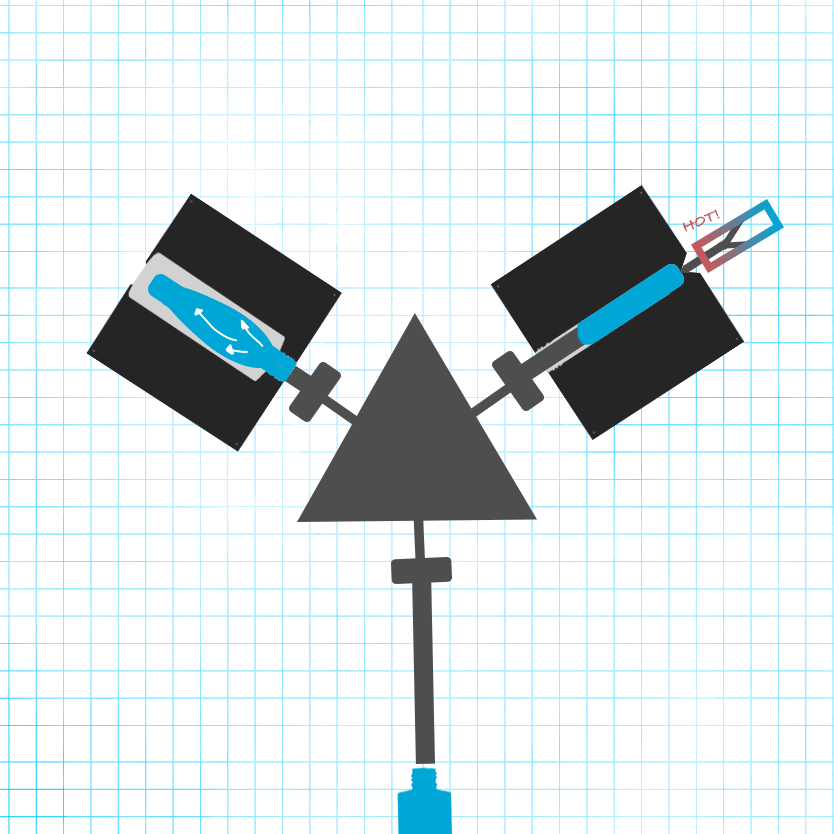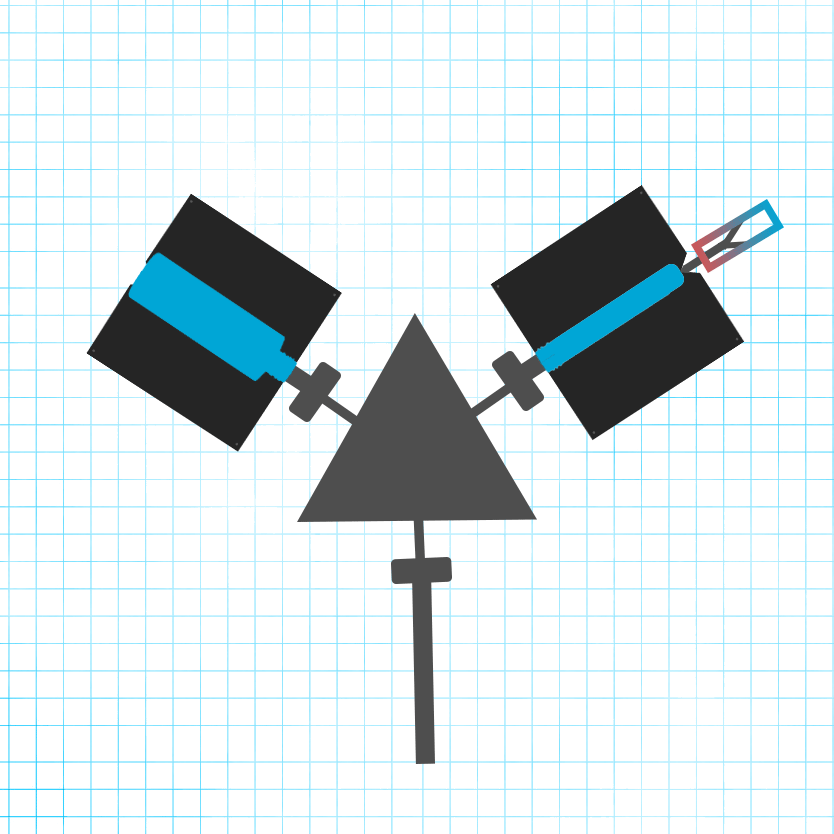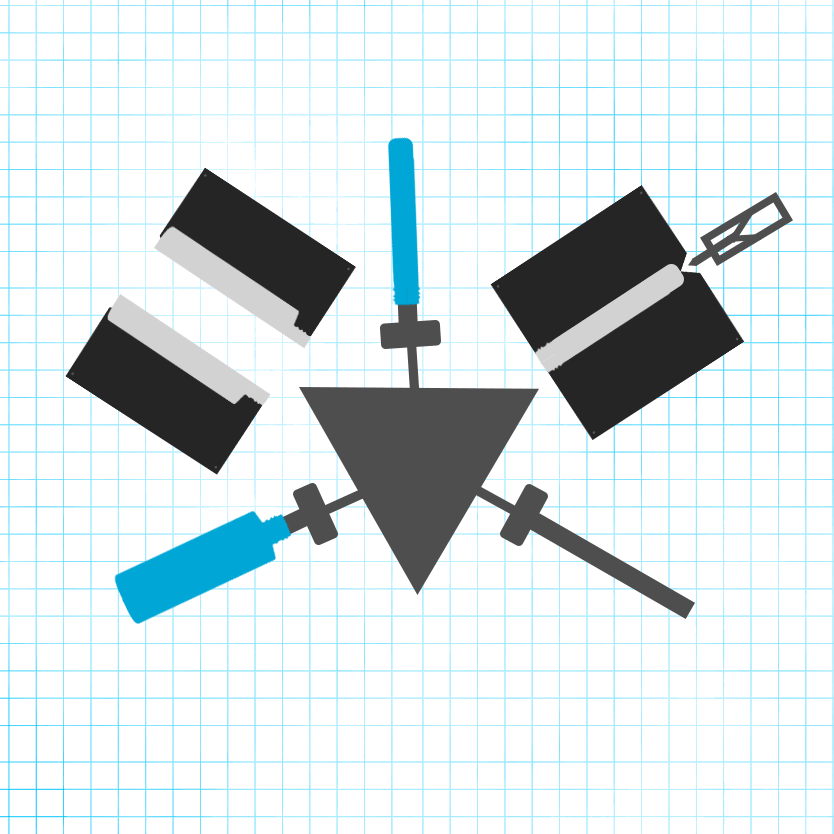
IBM is capable of holding tighter neck dimensions and maintaining a more precise gram weight compared to EBM. Here’s how it works:
Preform Injection: Plastic is injected into injection mold cavities, forming preforms that resemble test tubes with defined necks.
Transfer to Blow Mold: The preforms are transferred to blow mold cavities.
Blow Molding: In the blow mold, the preforms are blown into the final bottle shape.
 Cooling and Ejection: After cooling, the bottles are ejected. IBM typically results in a “gate bullseye” at the bottom of the bottle, with potential parting lines along the sides.
Cooling and Ejection: After cooling, the bottles are ejected. IBM typically results in a “gate bullseye” at the bottom of the bottle, with potential parting lines along the sides.
Injection Stretch Blow Molding (ISBM) or Stretch Blow Molding #
ISBM, often used for PET, can be a one-step or two-step process:
-
- One-Step ISBM: This process is employed for specialty applications requiring unique neck or preform shapes, such as handleware. The entire process, from forming preforms to blowing bottles, takes place within a single machine.
-
- Two-Step ISBM: Commonly used for beverage bottles, this process involves preforming the parison and neck, ejecting and cooling them to create “preforms,” and then inserting these preforms into the blow mold to achieve the final bottle shape. Two-step ISBM is favored for high-volume runs, as it allows for lightweighting.
Co-Extrusion (Co-Ex) #
Co-extrusion blow molding produces multi-layered bottles. Different layers are extruded together in the parison, creating a bond. Co-Ex can be used for cosmetic effects (e.g., adding a soft-touch matte finish) or enhancing barrier properties (e.g., incorporating PCR on the outer layer and virgin material on the inner layer).
Injection Molding (IM) #
Injection molding is rarely used for bottles but finds application in specialty cases where extremely tight tolerances are required. In this process, plastic is injected into a closed mold, creating a part with precision. Injection molding may be used for straight-walled containers or specific applications, such as inner airless bottles that require threading on both the inside and outside of the neck.
In conclusion, the manufacture of plastic bottles is a diverse field, with various processes tailored to specific needs. Understanding these processes empowers you to make informed decisions about the best manufacturing method for your unique bottle requirements. COMPAX is ready to assist you in navigating this intricate landscape and delivering top-quality plastic bottles that meet your brand’s objectives.




